Contact Centre
Knowledge Base
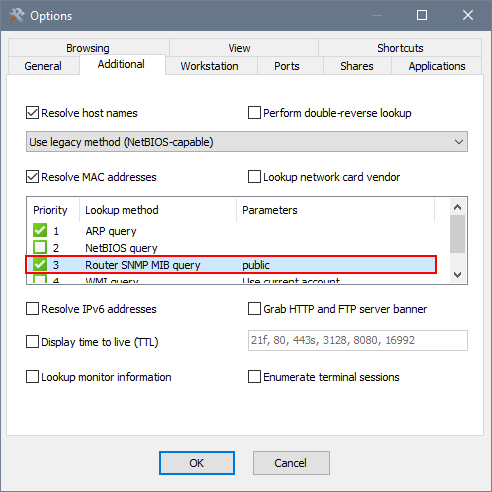
Configuring SNMP MIB query for MAC address resolution
It is possible to resolve MAC addresses in a different subnet if the router between the subnets exposes its ARP cache via SNMP. In this case the Network Scanner can pull the router's ARP tables and match IP addresses to MAC addresses.
Since a router sits between subnets and knows clients MAC addresses on each side, this method works for both local and non-local subnets. The router may need to be specially configured to provide this information via SNMP.
There are three common OIDs (Object Identifiers) where SNMP-capable routers keep IP-to-MAC-address mapping tables:
- iso.org.dod.internet.mgmt.mib-2.ip.ipNetToPhysicalTable
- iso.org.dod.internet.mgmt.mib-2.at.atTable.atEntry
- iso.org.dod.internet.mgmt.mib-2.ip.ipNetToMediaTable
Your router needs to support at least one of these, have SNMP enabled and a community string set.
After enabling the Router SNMP MIB query option, double-click the option and specify a read community string (similar to a password) and the router's IP address, as shown below.
After that, the Network Scanner will attempt to make an SNMP connection to the specified IP address(es) using the community string as a password and, if successful, enumerate the above tables that contain IP-to-MAC-address mappings. This is done before scanning the network, so at the time of scanning the application already knows which IP address corresponds to which MAC address and can display them.
Related articles:
← Go back