Image files
An image file is a regular file that contains an image of a disk.
Usually, RAM disks are volatile and used precisely because they erase all their contents after the computer is turned off. However, some users require the contents of a RAM disk to be kept. In this case, an image file can be used for saving the contents of a RAM disk before the computer is turned off, and restoring the contents back to the RAM disk when it is turned on next time.
The RAM Disk software uses its own format for image files. These image files can either be mounted as regular disks for copying files onto them, or serve as a base for RAM disks.
To begin working with an image file, you need to create it first by choosing Image – Create Image from the main menu. Specify the name of the image file with the full path to its location, and the size. This size should not exceed the amount of RAM that you can dedicate to a RAM disk, because the size of the image determines the size of the RAM disk based on this image. If you are planning to use hard disk emulation, select the Hard Disk image type; otherwise leave it as Volume. Optionally choose the file system and specify the volume label:
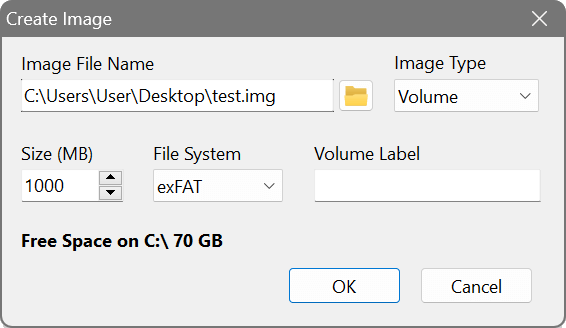
The newly created image file is blank and does not contain any file system unless you chose one in the previous step. Therefore, the next step is to mount the image and format it:
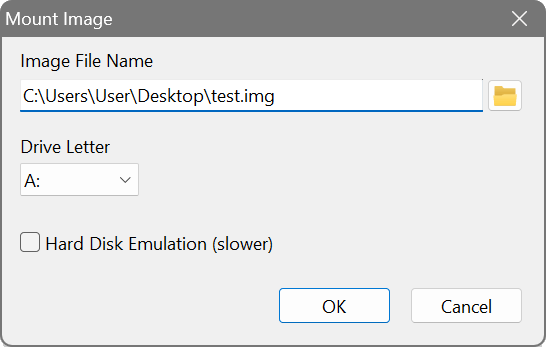
Use Windows Explorer or other tools to format the disk (disk A:\ in this example) and copy whatever files you would like to store in the image. Once you have finished with this, unmount the image by selecting Image – Unmount Image from the main menu:
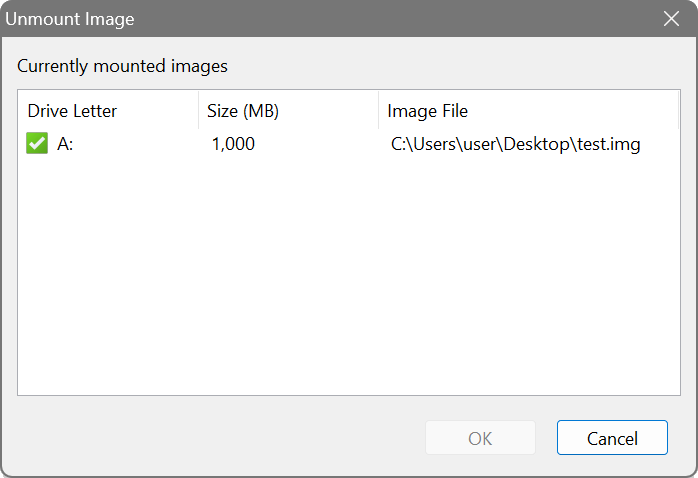
Your image file is now ready to be used as a base for a RAM disk. See adding a RAM disk on how to associate a RAM disk with the image file.